Human diseases transmitted by dog poop
From bacteria
Campylobacteriosis symptoms include diarrhea, cramping, abdominal pain, and fever. The illness typically lasts one week but for people with compromised immune systems, Campylobacter can spread to the bloodstream and result in a life-threatening infection.
E. Coli and other fecal coliforms live in the intestines of many animals. Certain strains can escape into the bloodstream, or cause stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. For people with weakened immune systems, E.coli infection can result in death.
Salmonellosis is the most common bacterial infection transmitted to humans by other animals. Symptoms include fever, muscle aches, headache, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Yersiniosis is another bacterial disease that can cause intestinal infections in people. Yersinia can multiply in cold water, unlike many other bacteria and may be found in elevated numbers in ponds, puddles and lakes as they thaw in the spring.
From parasites
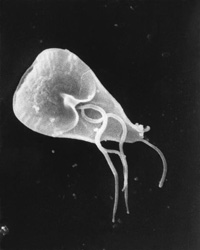
Giardia cell
Cyclospora infection usually incubates in the body for a week and then causes gastroenteritis that can wax and wane for over a month.
Cryptosporidium and Giardia microscopic parasites found in water. They can cause intestinal diseases (giardiasis or "beaver fever " and cryptosporidiosis).
Roundworm (including hookworm and whipworm) larva can migrate throughout the body to the brain, lungs, kidneys, liver, heart, or eyes. Roundworm larva can cause blindness.
Tapeworms can infect humans through the pores of their skin or by being ingested. They attach to the intestines and absorb nutrients from their host.
Toxoplasmosis, a parasite carried by cats, can cause birth defects if a woman becomes infected during pregnancy or for people with depressed immune systems.
